Localization of XML Files in Wordbee
About GlobalVision
This blog post was contributed by GlobalVision International, Inc. a software localization and translation service provider. You can find similar posts on translation, localization technology, website globalization and medical translation trends on the company’s blog: GlobalEyes.
Ed. Note. Thanks to GlobalVision for this post. They are one of the pre-eminent providers of software localization services in the USA. If you are struggling with software localization, you can count on GlobalVision for excellent results.
In the previous blog we discussed how to localize CSV and XLS files in Wordbee. In this post, we will tackle the localization of XML files.
If you are involved in translating database content, online help and web help, you will find yourself facing XML. It is also important to note that DITA, XLIFF and TMX are all XML-based formats.
Web-enabled software apps often contain a database component that can only be exported in XML. Furthermore, content management systems export content in XML. When the content needs to be localized, you will be faced with the task to parse the XML output.
Why is XML so Popular?
eXtensible Markup Languages (XML) is known to be both human and machine readable. It is a metalanguage that enables users to define their own customized markup language. Unlike HTML, which was designed to describe presentation, XML describes content. This is why XML has become the de facto standard in content management systems, particularly with authoring tools that are object-oriented. XML helps manage single-sourced content very effectively. The fact that content has become extensively embedded in XML code makes localization of XML files a necessity that no translation and localization professional can escape.
What Does XML Look Like?
XML looks very much like HTML. But with XML, you can build and define more markup to fit the purpose of the data that it contains. Given its power and flexibility XML is also supported on many platforms for structuring and exchanging data. XML documents must contain one root element that is the parent of all other elements and these elements can contain data, other elements, a combination of both, or neither as in an empty element. All XML documents have a single root element which contains sub-elements, and their sub-elements…
Challenges Translating XML Files
When it comes to translating XML files the first thing to do is to identify which elements contain the text to be translated. Then, one needs to identify the parts of the content that require translation, hence protecting all other elements and their associated text from modification.
Content of translatable XML elements may also contain attributes to define conditions on when these elements are to be translated or not. Once identified, the text to be presented to translators in the editor may be complex and may contain embedded markup code [HTML], Cdata or even customized variables.
All these elements need to be analyzed and identified if they need to be translated or should remain in the source language.
What is unique in Wordbee is its ability to make almost any XML content very easy to parse and imposes no artificial restrictions on the XML content. This allows software developers and technical writers to add text inside the XML elements without giving a second thought about causing localizers problems while parsing the files. This unshackles developers’ hands and enables them to be as creative as possible. Any code or syntax can hence be part of the text. Wordbee can mark them as untranslatable or convert them to tags.
Why Use Wordbee When Localizing XML Files?
Wordbee offers in the XML configuration many settings. They allow users to account for all elements and make sure that only the text that needs translation is available in the Editor. This text is what translators will see and translate, eliminating errors in code alteration.
With the XML setting you can also define the nodes that need to be extracted for translation and the nature of their content. Wordbee selects and defines the XML nodes by means of Xpath expressions and the Xpath builder tool. The tool assists users in creating Xpath expressions when they are unexperienced in writing them.
Additional settings are also available for more complex text. Regular expressions can be used for any piece of text in the segments that need to be defined as either translatable or untranslatable.
Single words, terms or portions of a segment can be excluded from translation. Furthermore, the text captured by regular expressions is converted to markup and thus protected from modification.
If your XML contains translatable HTML, the HTML is then processed according to a specific configuration that the user selects. All HTML markup is hence protected in the translation editor.
What Do XML Files Look Like in Wordbee?
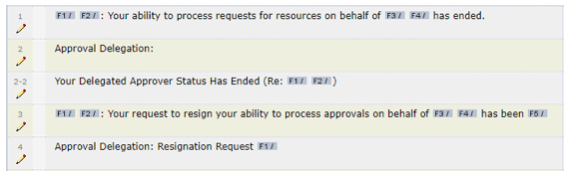
In our above example for instance, only two elements will need to be translated:
- NOTIFICATION_SUBJECT, and
- NOTIFICATION_BODY, but only if type =’clob’. Any other attribute does not need translation.
Any words surrounded by the % signs are custom variables and need to be converted to inline tags.
By applying the proper settings in Wordbee, below are the strings that will show up in the Wordbee editor for translation.
Note how all the markup, tags, variables and other code are hidden. This will ensure that translators do not mistakenly or by accident translate or change any of it. By making sure that only the text that the user sees is translated, endless hours of quality assurance and quality control are eliminated.
Other Benefits of Using Wordbee for XML Localization
Localizing XML is a critical part of handling software localization tasks properly. But once the XML is translated, you want to make sure that the code is intact and exports correctly.
Wordbee offers QA Checks in batch mode to check for the following:
- Missing or invalid markup. It checks target against source and flags any missing or incorrect markup. This avoids errors in tags undetected or introduced by translators.
- Detected double spaces. Translators introduce at times two spaces by mistake. This will help you remove them. This is important particularly when screen real estate is tight.
- Inconsistent leading and trailing spaces. It eliminates any leading or trailing spaces.
- Missing spaces at segmentation boundaries. This will eliminate the presence of merged words due to a missing space between them.
Also, Wordbee enables the translator to preview the source and target languages while performing the translation to get an idea of what the source or translated content will look like once completed.
When all these Wordbee features are properly used by your software localization service provider, your localized XML content will function right out of the box. This will potentially save you endless hours formatting and debugging when generating your software, online help or even your printed manuals.
Is this interesting?
Subscribe to get interesting localization podcasts, discussion panels, and articles every month.